Process of thin-walled parts
Thin-walled sleeve parts are always prone to deformation during processing, and there are oval or small middle and large waist shapes at both ends, which makes it difficult to guarantee the processing quality of the parts. Its clamping design is often one of the most discussed points. Let's take a look at two examples of thin-wall fixture design in turning and milling, and how they solve the deformation problem.
Part.1 Machining scheme of thin-walled sleeve parts on milling machines
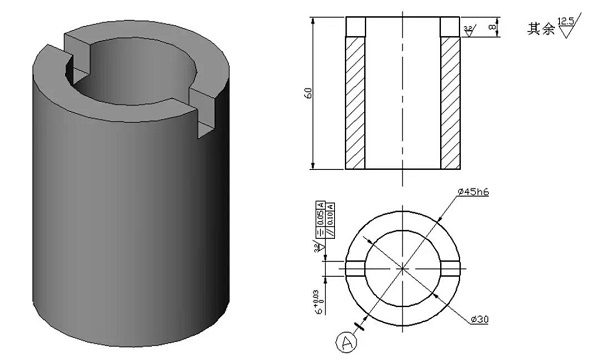
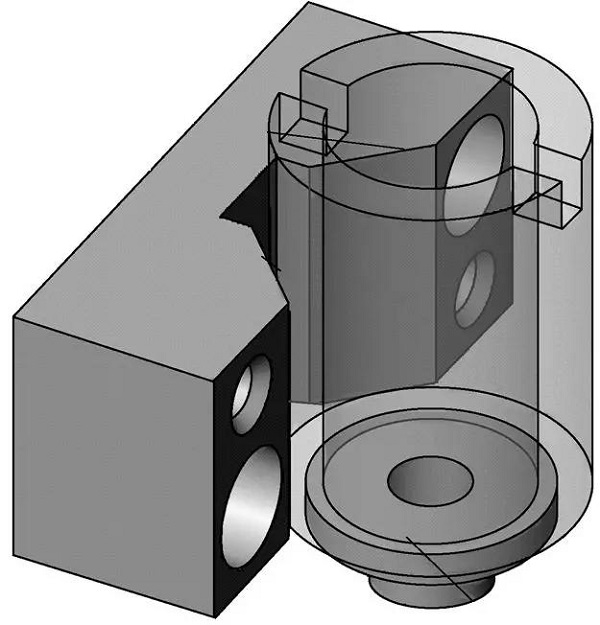
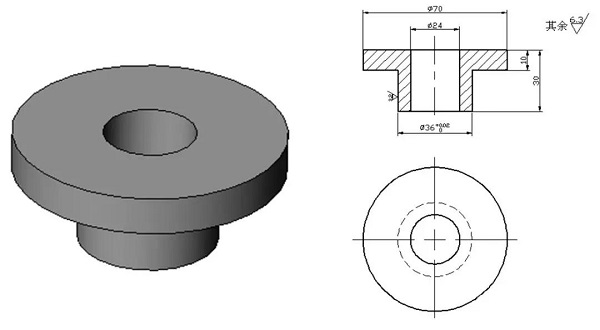
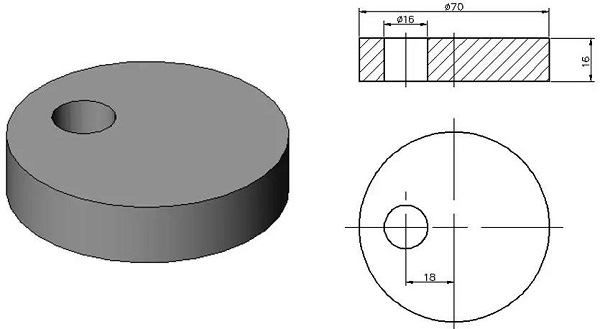
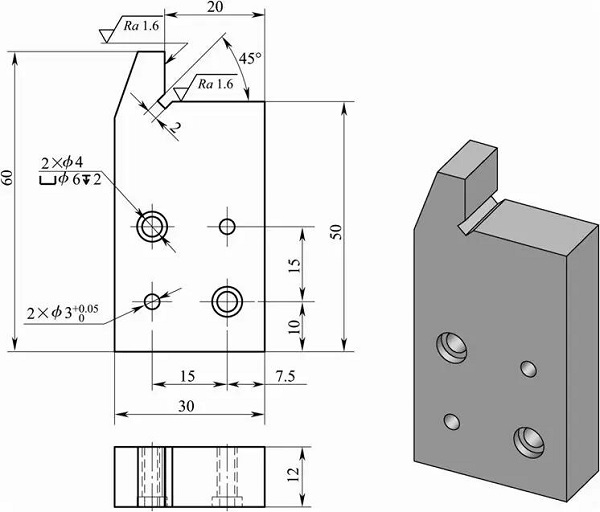
The thin-walled sleeve workpiece is shown in the figure. The key slot width of 6mm is guaranteed by the key slot milling cutter; the symmetry of the symmetrical plane on both sides of the groove to the φ45h6 axis is 0.05mm and the parallelism is 0.10mm; the groove depth is 8mm.
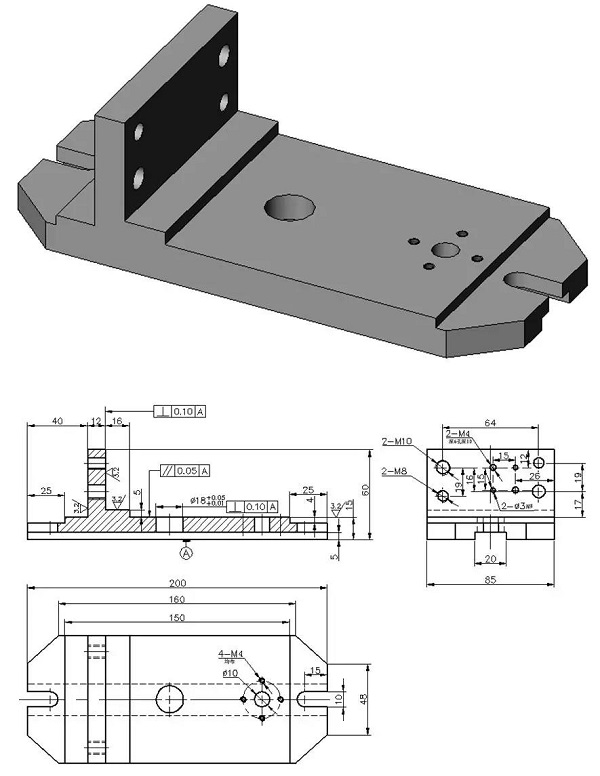
Positioning scheme and positioning components
Determine positioning scheme and choose positioning components:
Design of clamping scheme and clamping device
Design of fixture structure
Positioning device
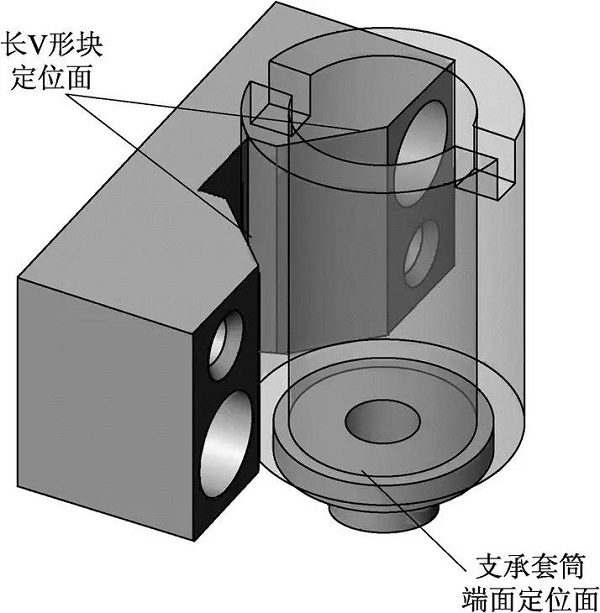
The long V-shaped block is the main positioning element in this fixture, eliminating 4 uncertainties of the workpiece. Can be found in relevant national standards or industry standards.
Support sleeve:
2. Clamping device
3. Auxiliary device
4. Clip specific
5.Overview of fixture
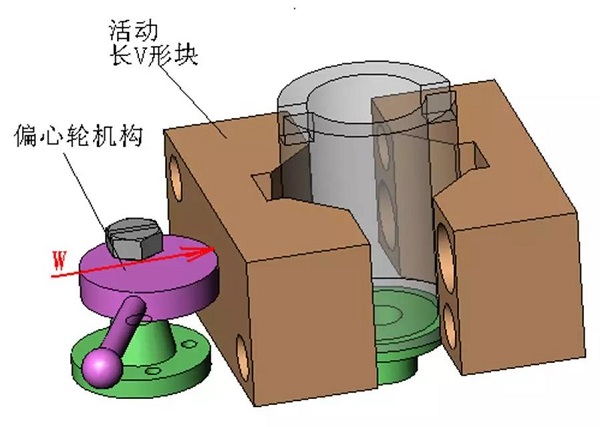
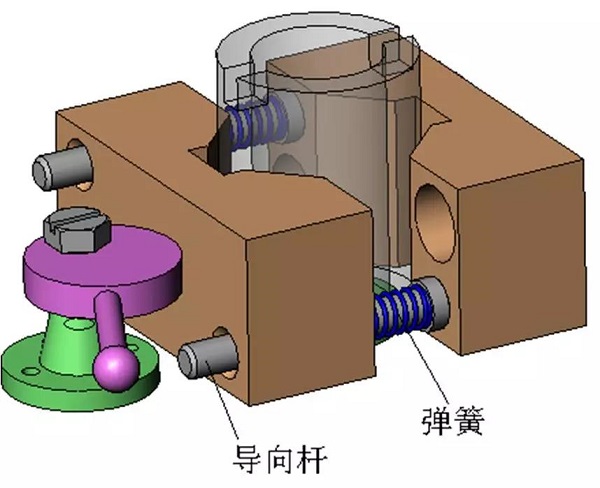
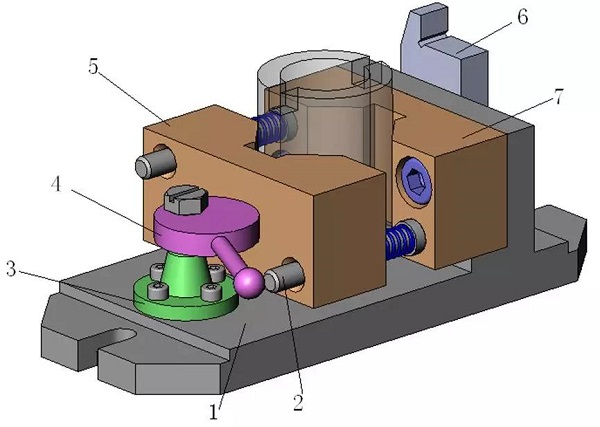
1. Clip specific 2. Cylindrical pin 3. Eccentric wheel bracket 4. Eccentric wheel 5. Movable V-shaped block 6. Knife block 7. Fixed V-shaped block
Part.2 Process plan for inner hole processing of thin-walled parts
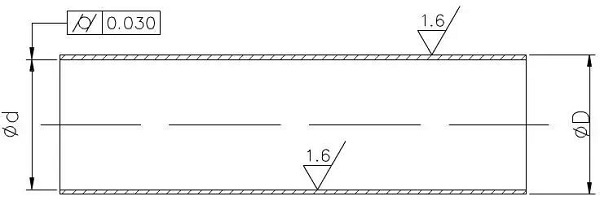
The workpiece is processed by seamless steel tubes. The surface roughness of the inner hole and the outer wall is Ra1.6 μm, which can be achieved by turning. However, the cylindricalness of the inner hole is 0.03 mm, which requires higher requirements for thin-walled parts. In mass production, the process route is roughly: blanking-heat treatment-car end face-car outer circle-car inner hole-quality inspection.
Internal hole processing is the key to quality control. It is difficult to guarantee a cylinder of 0.03mm when we cut the inner hole without the outer circle and thin-walled sleeve.
Key technology of car hole
The key technology of turning is to solve the problems of rigidity and chip removal of inner turning tools. To increase the rigidity of the inner hole turning tool, take the following measures:
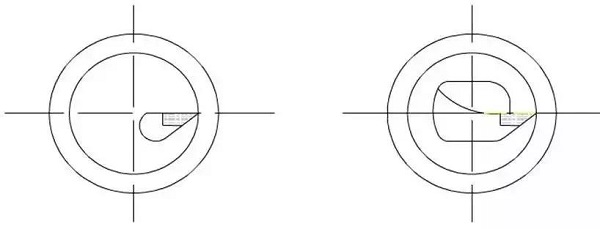
1. Increase the cross-sectional area of the shank as much as possible, usually the tip of the inner hole turning tool is located on the top of the shank, so that the cross-sectional area of the shank is less and less than 1/4 of the cross-sectional area of the hole. If the tip of the inner hole turning tool is located on the center line of the shank, the cross-sectional area of the shank in the hole can be greatly increased, as shown in the right figure below.
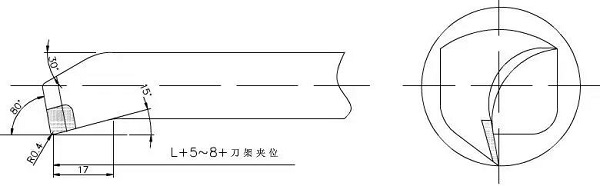
2. The length of the tool holder extension can be as long as the length of the workpiece to be processed is 5-8mm, so as to increase the rigidity of the tool holder and reduce the vibration during the cutting process.
Solve chip removal problems
The main control is the cutting outflow direction. The rough turning tool requires the chips to flow to the surface to be processed (front chip). For this reason, a positive-angle inclination turning tool is used, as shown in the figure below.
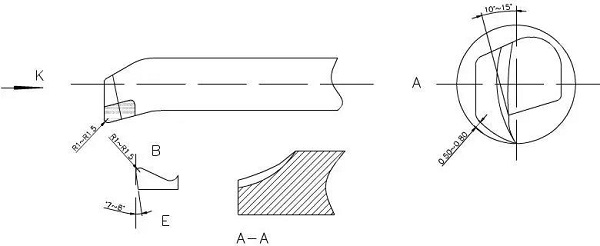
When finishing turning, it is required that the chips flow toward the center and the chips are discharged forward (hole chip removal). Therefore, pay attention to the grinding direction of the cutting edge when sharpening the knife. Blade alloy YA6, the current M type, its bending strength, abrasion resistance, impact toughness, and anti-adhesion and temperature with steel are good.
When sharpening, the front angle grinds in a circle with an arc-like angle of 10-15 °, and the back angle is 0.5-0.8mm away from the wall according to the processing arc (the tool bottom line is in radian). The chip B-point smoothing edge is R1-1.5, and the auxiliary rear angle is ground to 7-8 °, and the AA point of E inner edge is ground to discharge chips outward.
processing method
1. A shaft guard must be done before processing. The main purpose of the shaft guard is to cover the inner hole of the thin wall sleeve of the car in its original size, and fix it with the front and rear centers so that it can process the outer circle without deformation, and maintain the quality and accuracy of the outer circle processing. Therefore, the processing of the shaft guard is a key link in the process of processing thin-walled casing.
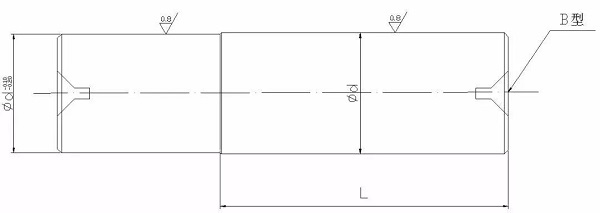
45 ﹟ carbon structural round steel is used for processing the shaft protection blank; the end face of the car is opened with two B-type top holes, and the car is rounded with a margin of 1mm. After heat treatment, quenching, tempering, and shaping, leave 0.2mm for grinding. Re-heat-treat the crushed fire surface with hardness HRC50, and then grind it with a cylindrical grinder as shown in the figure below. The accuracy meets the requirements and will be used after completion.
2. In order to allow the workpiece to be processed at one time, the blank will be clamped and cut off.
3. The heat treatment is used for tempering and setting of the hair embryo first, and the hardness is HRC28-30 (hardness that can be processed).
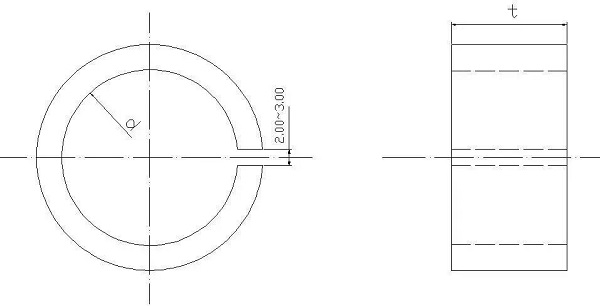
4. The turning tool uses C620. First, the front tip is fixed in the spindle cone position. To prevent deformation of the workpiece when clamping the thin-walled sleeve, an open-loop thick sleeve is added, as shown below.
In order to maintain mass production, the outer end of the thin-walled sleeve is processed to a uniform size d, and the ruler of t is an axial clamping. The thin-walled sleeve is pressed to improve the quality of the inner hole of the car and maintain the size. Considering the generation of cutting heat, it is difficult to grasp the size of the workpiece expansion. Need to pour sufficient cutting fluid to reduce thermal deformation of the workpiece.
5. Use the self-centering three-jaw chuck to clamp the workpiece firmly, the car end face, and the rough car inner circle. Remaining amount of 0.1-0.2mm precision turning, change the finishing allowance to the machining allowance of the cutting shaft to full over-fitting and roughness requirements of the guard shaft. Remove the inner hole turning tool, insert the guard shaft to the front center, use the tailstock center to clamp according to the length requirement, change the outer turning tool to the rough turning of the outer circle, and then finish turning to the drawing requirements. After passing the inspection, use a cutter to cut it to the required length. In order to smooth the cut when the workpiece is broken, the cutting edge should be obliquely sharpened to make the end surface of the workpiece flat; the smaller part of the guard shaft is ground to cut off the gap and reduce the size of the workpiece. The injury was caused by falling.
The above method for processing thin-walled sleeves solves the problem of deformation or dimensional and shape errors that do not meet the requirements. Practice has proved that the processing efficiency is high, easy to operate, and suitable for processing long thin-walled parts. The size is easy to grasp. It is completed in a second time and mass production is more practical.