Common metal forming processes
1. Planing processing—It is a cutting processing method that uses a planer to horizontally and linearly reciprocate the workpiece. It is mainly used for the shape processing of parts. The precision of the planing process is IT9 ~ IT7, and the surface roughness Ra is 6.3 ~ 1.6um.

2. Grinding-Grinding refers to the processing method of removing excess material on the workpiece with abrasives and tools. Grinding is one of the more widely used cutting methods.
3. Selective laser melting—In a tank covered with metal powder, a computer-controlled beam of high-power carbon dioxide laser selectively sweeps the surface of the metal powder. Wherever the laser goes, the metal powder on the surface layer is completely melted together, and the powder state remains where it is not. The entire process needs to be carried out in a sealed tank filled with inert gas.

4. Selective laser sintering-the SLS method uses infrared lasers as energy sources, and the modeling materials used are mostly powder materials. During processing, the powder is first preheated to a temperature slightly below its melting point, and then the powder is flattened by the scraping stick; the laser beam is selectively sintered according to the layered cross-section information under computer control, and one layer is completed After that, the next layer is sintered. After all the sintering is completed, the excess powder is removed, and a sintered part can be obtained. Currently mature process materials are wax powder and plastic powder, and the sintering process using metal powder or ceramic powder is still under study.

5. Metal deposition—Similar to creamy fused deposition, but sprayed with metal powder. The nozzle ejects the metal powder material while providing high-power laser and inert gas protection. In this way, it is not limited by the size of the metal powder box, it can directly manufacture larger parts, and it is also very suitable for repairing locally damaged precision parts.
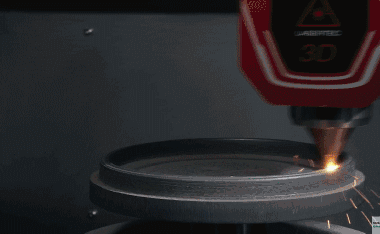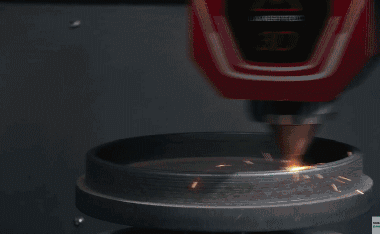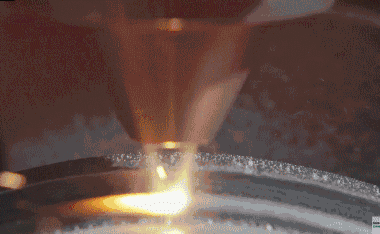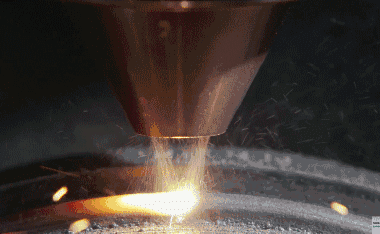
6. Roll forming-The roll forming method uses a set of continuous stands to roll stainless steel into complex shapes. The sequence of the rollers is designed such that the roll pattern of each stand continuously deforms the metal until the desired final shape is obtained. If the shape of the part is complex, a maximum of 36 racks can be used, but for a simple part, three or four racks are sufficient.
7. Die forging—refers to the forging method of obtaining forgings by using the mold to form the blank on the special die forging equipment. Forgings produced by this method are accurate in size, have small machining allowances, and have complex structures and high productivity.

8. Die-cutting—that is, the blanking process, positioning the film formed in the previous process on the die of the punching die, closing the mold to remove excess material, retaining the 3D shape of the product, and matching the mold cavity.
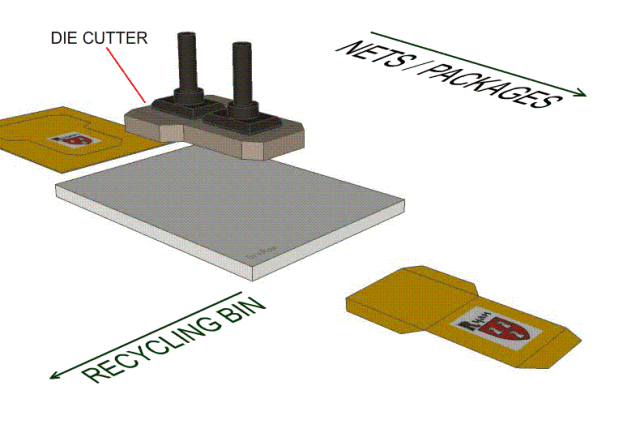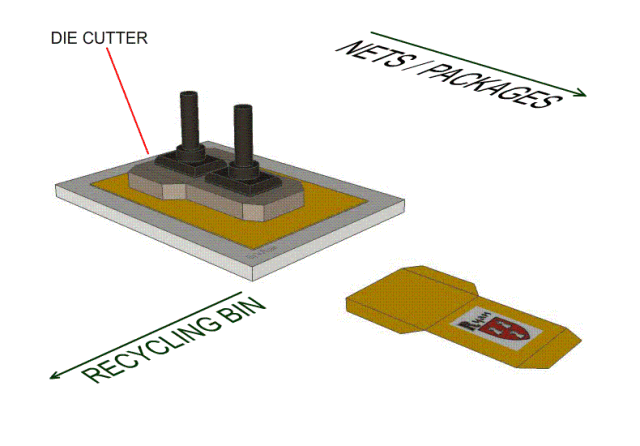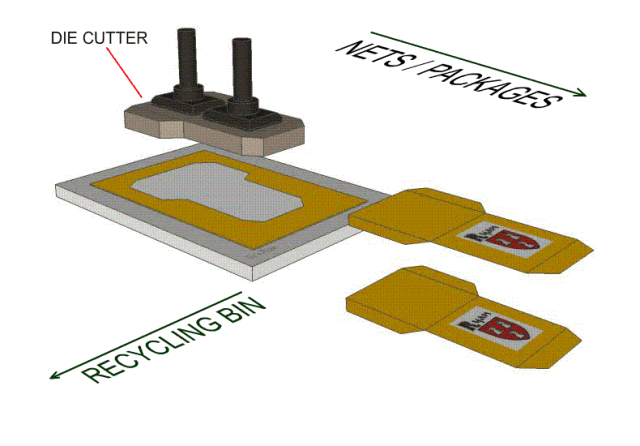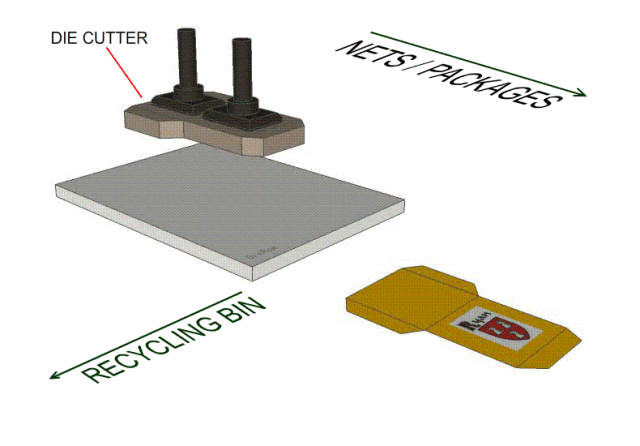
9, die-cutting process-knife die-knife die blanking process, positioning the film panel or circuit on the bottom plate, the knife die is fixed on the machine template, using the force provided by the machine to control the blade to cut the material. What distinguishes him from the punching die is that the cut is smoother; at the same time, by adjusting the cutting pressure and depth, it can punch out the indentation and half-break. At the same time, the low cost of the mold makes the operation more convenient, safe and fast.

10. Centrifugal casting is a technique and method for injecting liquid metal into a mold that rotates at a high speed, so that the metal liquid is filled with the mold under the action of centrifugal force and forms a casting. The mold used for centrifugal casting, depending on the shape, size and production batch of the casting, can be used non-metallic (such as sand, shell or investment shell), metal or coated with a coating or resin sand in the metal Mold.

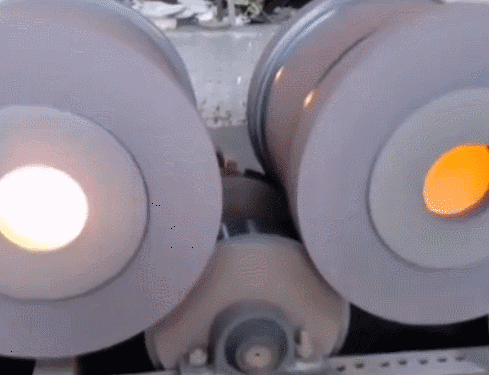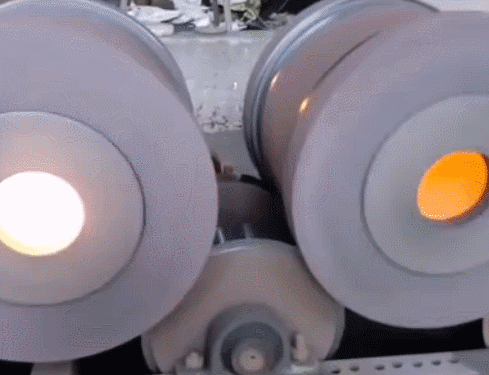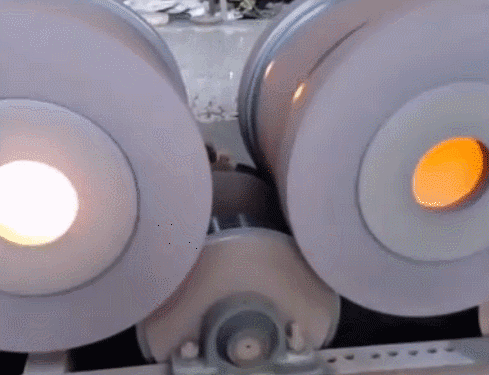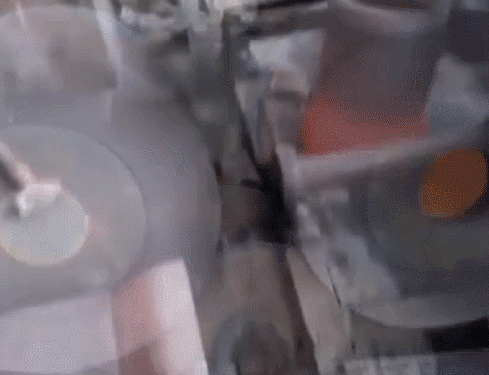
11. Lost foam casting—It is a combination of paraffin or foam models similar to the size and shape of the casting to form a model cluster. After brushing with refractory paint and drying, it is buried in dry quartz sand and vibrated in shape. The model is vaporized, and the liquid metal occupies the position of the model. A new casting method is formed after solidification and cooling. Lost foam casting is a new process with almost no margin and precise forming. This process does not require mold removal, no parting surface, and no sand core, so the casting has no flash, burrs, and draft angle, and reduces Dimensional error caused by combination.

12. Squeeze casting-also known as liquid die forging, is to make molten metal or semi-solid alloy directly injected into the open mold, and then close the mold to produce a filling flow to reach the external shape of the part, and then apply high pressure to make The solidified metal (shell) is plastically deformed, and the unsolidified metal is subjected to isostatic pressure and high-pressure solidification at the same time. Finally, the method of obtaining a product or blank is directly squeeze casting; indirect squeeze casting refers to the molten state A method of injecting metal or semi-solid alloy into a closed mold cavity through a punch and applying high pressure to crystallize and solidify under pressure, and finally obtain a product or blank.
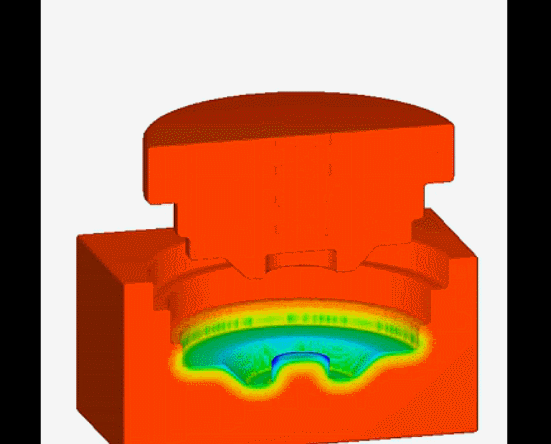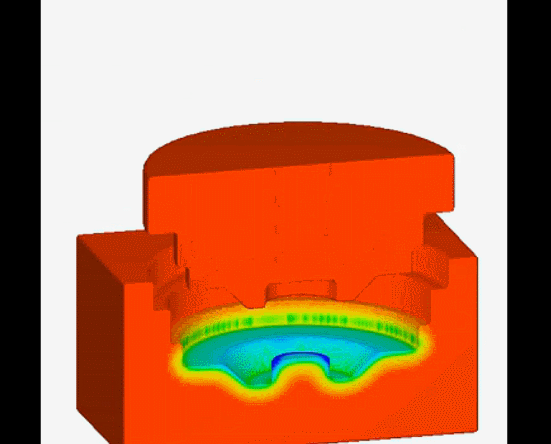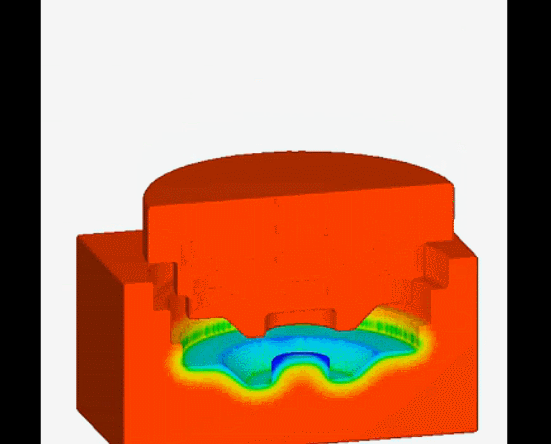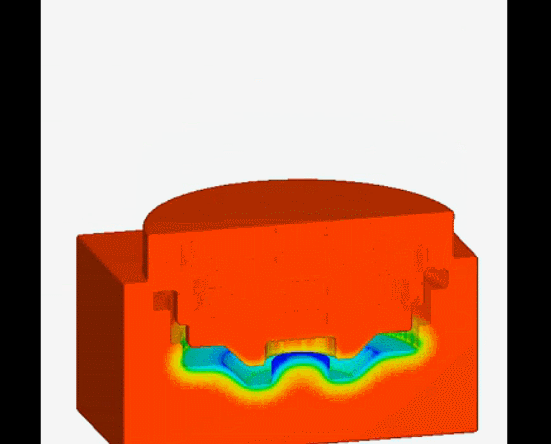
13. Continuous casting-is a casting method in which a continuous mold is used to continuously pour liquid metal at one end and continuously pull out the molding material from the other end.

14. Drawing—It is a plastic processing method that uses external force to act on the front end of the pulled metal, and pulls the metal blank from the die hole smaller than the cross section of the blank to obtain the corresponding shape and size of the product. Since drawing is performed in a cold state, it is also called cold drawing or cold drawing.

15. Stamping—It is a forming method that applies external force to the plates, strips, pipes and profiles by presses and molds to plastically deform or separate them, so as to obtain workpieces (stamped parts) of the required shape and size.
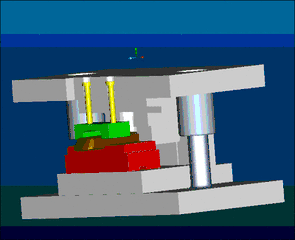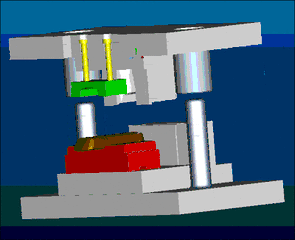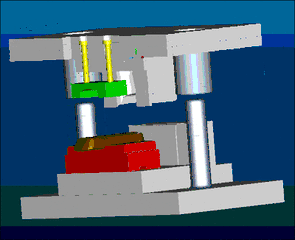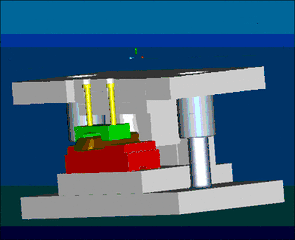
16. Metal Injection Molding, referred to as MIM for short, is a new type of powder metallurgy near-net forming technology extended from the plastic injection molding industry. As we all know, plastic injection molding technology produces various complex shapes at low prices, but the strength of plastic products It is not high. In order to improve its performance, metal or ceramic powder can be added to the plastic to obtain high strength and good wear resistance products. In recent years, this idea has evolved to maximize the solid particle content and completely remove the binder and densify the shaped body during the subsequent sintering process. This new powder metallurgy forming method is called metal injection molding.
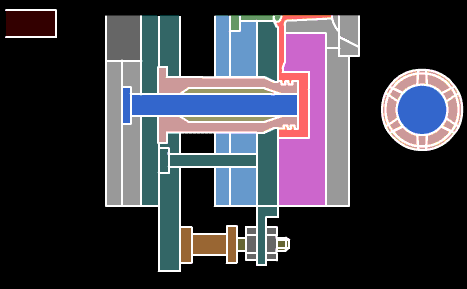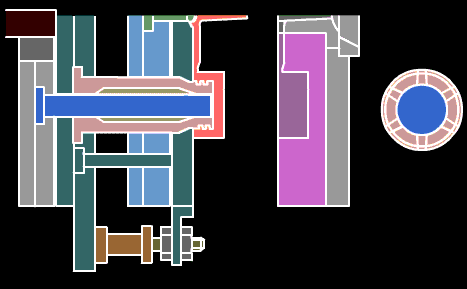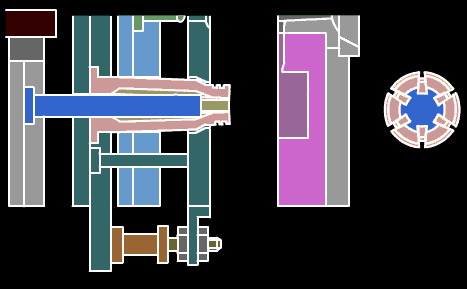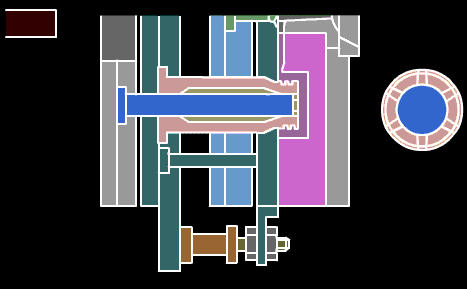
17, turning processing-refers to lathe processing is part of mechanical processing. Lathe processing mainly uses a turning tool to turn a rotating workpiece. Lathes are mainly used for machining shafts, disks, sleeves and other workpieces with rotating surfaces. They are the most widely used machine tools in machinery manufacturing and repair plants. Turning is a method of cutting a workpiece on a lathe by rotating the workpiece relative to the tool. The cutting energy provided by turning is mainly provided by the workpiece rather than the tool.
Turning is the most basic and common cutting method, which occupies a very important position in production. Turning is suitable for turning surfaces. Most of the workpieces with turning surfaces can be processed by turning methods, such as inner and outer cylindrical surfaces, inner and outer conical surfaces, end faces, grooves, threads and rotary forming surfaces. The tools used are mainly turning tools.






